NATIVE PLANT SEEDING
PURPOSE
To increase biodiversity, create pollinator habitat, restore soils, increase shade, and improve woodland health.
Ensure invasive species do not repopulate an area where they have been recently removed
Seeding can introduce a large number of potential plants and species into an area at low cost. It is most useful in areas where rapid plant establishment is not critical
SAFETY
Be aware of snakes, scorpions, or fire ants that may be living under rocks or logs.
Use sharp tools responsibly.
Stay aware of fellow workers to avoid hitting them with brush or tools.
Poison ivy is a common understory plant in many areas of the park. Avoid coming in contact with any part of this plant. Wear long sleeves and pants to avoid skin contact.
Tools Needed:
gloves
long-sleeved shirts and pants recommended
soap and/or lotion for poison ivy treatment
rake
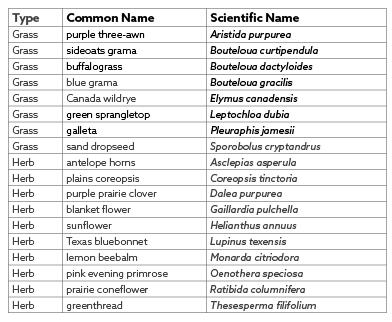
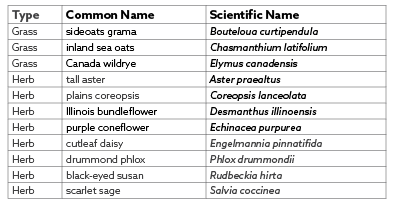
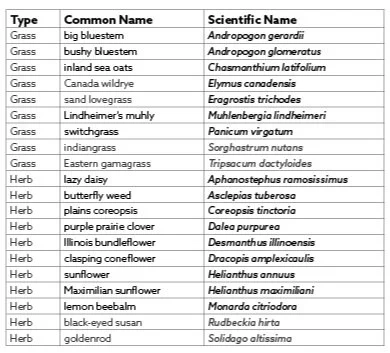
native seed (see seed lists below)
MATERIALS
METHODS
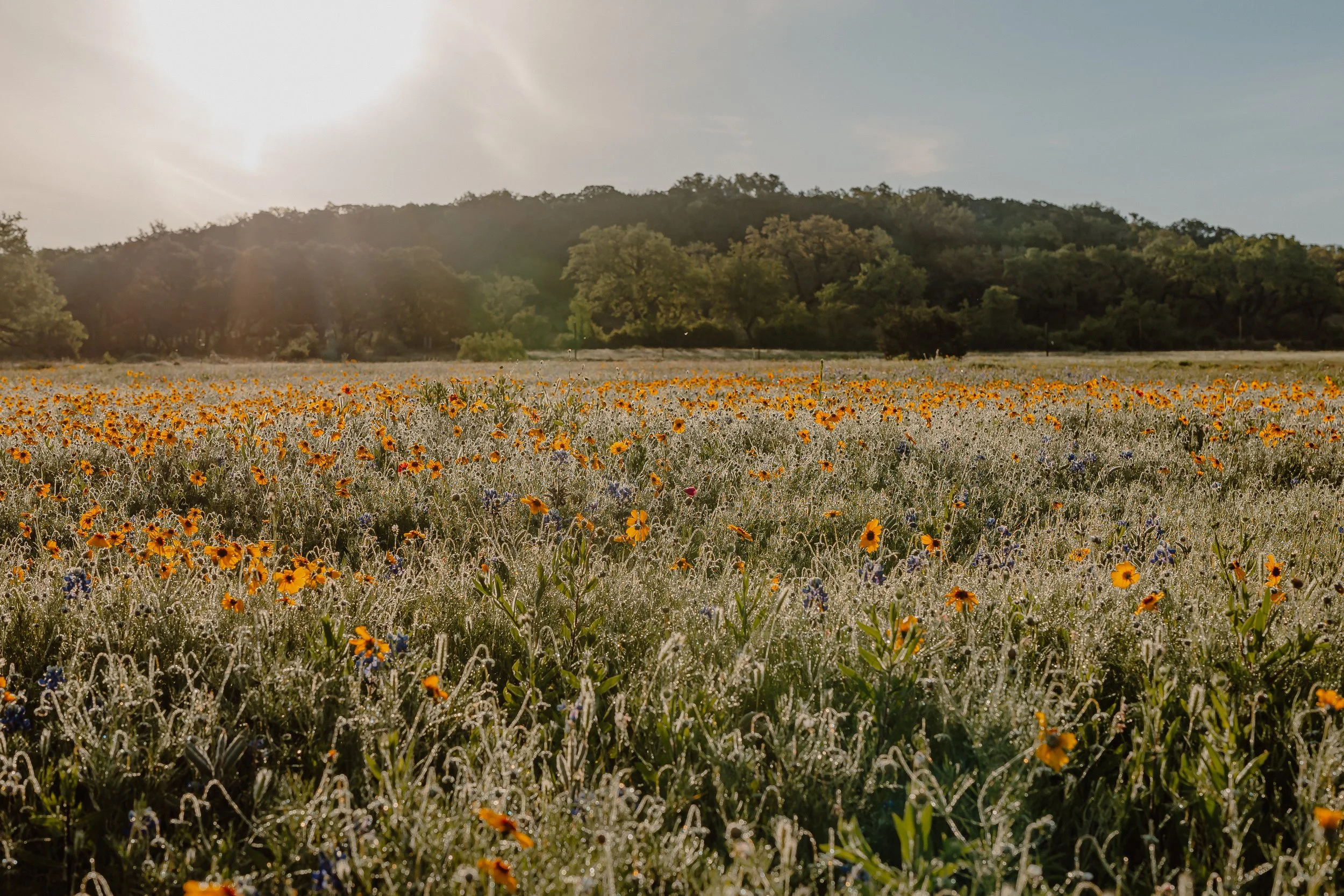
Identify the seeding area. Prioritize areas of recently-removed invasive species, low plant diversity, low canopy cover, high erosion, or high visibility.
Source seeds. Species should be native to the area and suited to the water and light availability. Seed rate should be between 20 and 40 lbs per acre, dependent on species, for areas of thin vegetation.
Establish clear boundaries with fences, rocks, logs, or brush that are durable and deter foot traffic. Plan for erosion and utilize logs, brush, or biodegradable straw logs to retain soil.
Most seeding should occur from October to March to allow plants to establish before the heat of the summer.
Clear the seeding area of leaf litter and duff layer to expose the soil. Lightly disturb the soil if it is soft, or actively break up the top 3-6” of soil if it is compacted. Retain all leaf litter and duff layer on site and replace following seeding.
Do not remove existing native plants. Leave native plants in place and seed around them.
Plan for maintenance. Long-term success requires that the new plants have sufficient water, are not being outcompeted by invasive species, and are not impacted by erosion issues.
NATIVE TEXAS SPECIES SUITABLE FOR RESTORATION
Includes species suitable for methods such as seeding, container planting, and live staking.
UPLAND FULL SUN SPECIES
UPLAND SHADE-DAPPLED SPECIES
MODERATE TO HIGH MOISTURE SPECIES
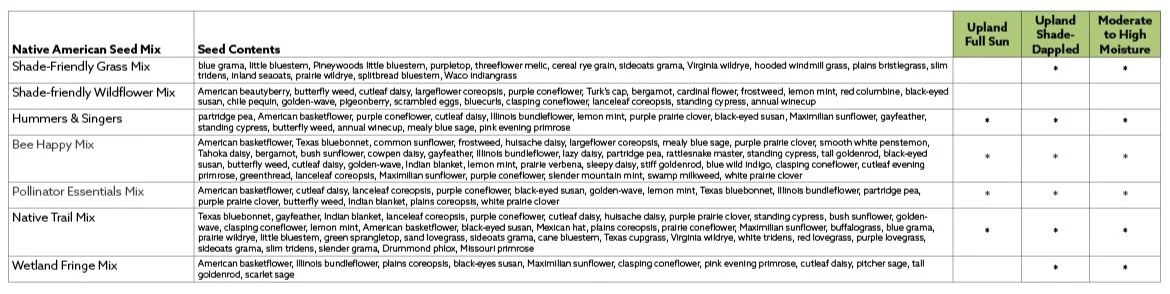
Approved Seed Vendors:
Native American Seed
Douglas King Seed
Turner Seed
For more approved seed mixes, reference Unified Stewardship Plan or City of Austin Standard Specification Manual 609S Native Seeding and Planting for Restoration